Please note: The content of this post is my own, unless the technical terms are too hard to explain, then the content is copied and pasted. I am not a medical professional and thus the post is my point of view. But the content is science-based and credible. Just because it is a new science, does not necessarily make it quackery. Always consult your doctor first before trying a new treatment.
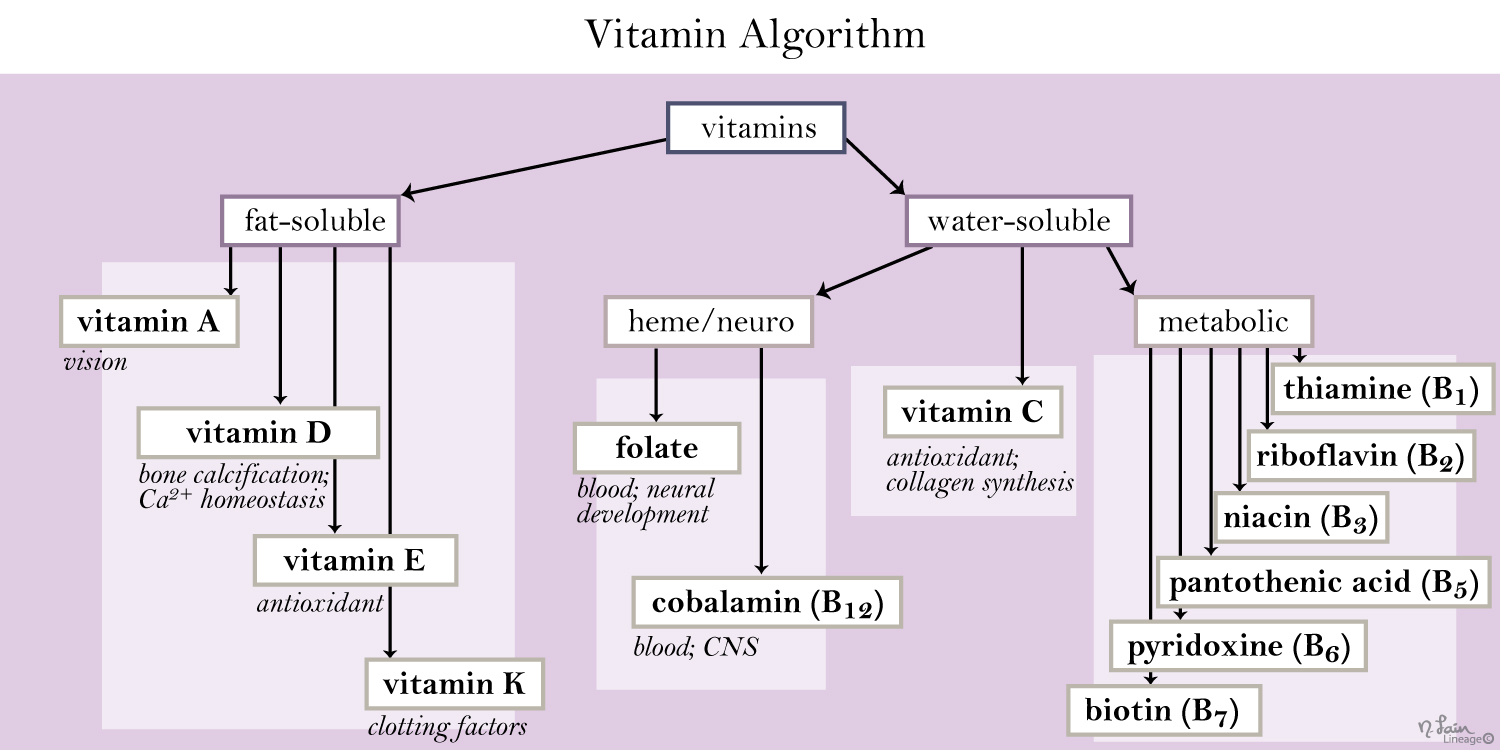
Previously we saw that your B vitamins are needed for most of your body’s systems, it is certainly very important in your methylation cycle.
We learned that Homocysteine is a sulfur-containing amino acid that can be converted to cystathionine and further to cysteine via the transsulfuration pathway (CBS) or remethylated to methionine. Also, Homocysteine is produced by the body by chemically altering adenosine.
To learn more about adenosine, click here.
 Do you Know?
Do you Know?
Migraine is a debilitating inflammatory blood vessel disease that may be triggered by damage inflicted by elevated blood levels of homocysteine to the endothelium of blood vessels in the brain.
Researchers have long suspected that migraine headaches have a genetic component because migraine sufferers often have family members who also have the condition. Studies suggest that MTHFR polymorphisms may account for the genetic predisposition to migraine in some individuals.
 Do you Know?
Do you Know?
Epilepsy also has a connection to elevated levels of Homocysteine.
Systemic administration of high doses of homocysteine in animals produce convulsive seizures, a fact that has been exploited in models of experimental epilepsy. Furthermore, up to 20% of patients with homozygous CBS deficiency have seizures, and the high plasma concentrations of homocysteine in these patients (usually 50-200 µmol/L) may contribute to epilepsy. Whether less severe hyperhomocysteinemia (15-20 µmol/L) predisposes patients to epilepsy has not been established.
Homocysteine relates to 2 additional important issues in the management of patients with epilepsy. First, most anticonvulsants lower plasma folate levels, and as a result, almost half of patients treated with anticonvulsants had homocysteine levels sufficiently elevated to put them at high risk for vascular disease. Arteriosclerosis is an important issue for patients requiring long-term anticonvulsant therapy, particularly given the rising incidence of epilepsy in older age groups. The effectiveness of polyvitamin therapy in lowering homocysteine levels in the setting of anticonvulsant use has not been directly studied.
A second issue relates to putative teratogenic effects of high homocysteine levels. There is an increased risk of major congenital malformations in children whose mothers receive anticonvulsants during the first trimester. While the mechanism of teratogenicity in folate deficiency is unclear, recent data implicate elevations in homocysteine. First, fasting or PML hyperhomocysteinemia is commonly found in women who have given birth to infants with neural tube defects. Second, the C677T mutation in the MTHFRgene significantly increases the risk of neural tube defects. Finally, amniotic fluid homocysteine levels were found to be significantly higher in pregnancies complicated by neural tube defects. Observations such as these led to a practice parameter recently promulgated by the American Academy of Neurology, recommending that all women of childbearing potential who are taking anticonvulsants consume at least 0.4 mg/d of folic acid. Whether this or higher doses of folic acid are effective in lowering homocysteine levels or in decreasing the incidence of neural tube defects in epileptic women has not been studied. It is also unclear whether cyanocobalamin and pyridoxine hydrochloride supplements are necessary for this population.
Read the full article on Homocysteine and Neurologic Disease here.
We have also seen that elevated homocysteine can be caused by drugs. However, a number of prescription drugs and natural compounds can also elevate the blood levels of homocysteine by interfering with folate absorption or metabolism of homocysteine. These include:
- Azaribine – Drugs used to treat or prevent skin disorders like psoriasis or for the routine care of skin. Also known as: AZARIBINE; Triazure; 2169-64-4; Triacetyl-6-azauridine; Azaribin; 6-Azauridine triacetate.
- Caffeine
- Cholestyramine – Cholestyramine is the active ingredient of Questran and Questran Lite. Cholestyramine is prescribed to lower high levels of blood cholesterol. It is a resin that binds to bile acids in the gut, thereby reducing its reuptake as well as the uptake levels of cholesterol in the blood. Cholestyramine is furthermore prescribed to treat some forms of diarrhoea. Cholestyramine reduces the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins including Vitamins A, D, E and K
- Colestipol – It prevents the bile acids from being recycled (reabsorbed) into your body. This action can be useful for people who have higher-than-normal levels of lipids in their blood. When the concentration of lipids in your blood is too high, it is called hyperlipidaemia. Also called Colestid®
- Colchicine – Colchicine is used for the treatment of gout. It affects the way the body responds to uric acid crystals, blocking the inflammation caused by them. Its other benefit is that it reduces the chance of future gout attacks if used in low doses. If nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are advised against, then colchicine is an effective alternative
- Fenofibrate – In the US, Fenofibrate (fenofibrate systemic) is a member of the drug class fibric acid derivatives and is used to treat Hyperlipoproteinemia (various levels and types) and Hypertriglyceridemia. Also brand name: Lipanthyl 200mg.
- Levodopa – The combination of levodopa and carbidopa is an anti-Parkinson agent. Levodopa increases dopamine levels in the brain, Carbidopa is combined with levodopa to prevent the breakdown of levodopa before it can reach the brain where it exerts its effect, thereby prolonging the effect of levodopa. Carbidopa also limits the side effects associated with levodopa. Also known as Carbilev, Madopar, Sinemet, Stalevo, Teva Carbi-Levo.
- Metformin – Metformin is used with a proper diet and exercise program and possibly with other medications to control high blood sugar. It is used in patients with type 2 diabetes. Metformin works by helping to restore your body’s proper response to the insulin you naturally produce. It also decreases the amount of sugar that your liver makes and that your stomach or intestines absorb
- Methotrexate – Methotrexate, sold under the brand name Methoblastin, is an antifolate drug, which means it inhibits the activation of folic acid in the body. It is taken once per week to treat a range of conditions. These include rheumatoid arthritis, the skin disorder psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease. This weekly therapy is known as “low-dose methotrexate”. Also know as Methotrexate-Lederle, P&U Methotrexate CSV injection,Abitrexate
- Niacin or Vitamin B3
- Nitrous oxide
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Pemetrexed – Pemetrexed (Alimta®) is a novel multitargeted antifolate that has activity against non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Also known as Terexta.’
- Phenytoin – Phenytoin sodium is an anticonvulsant. Anticonvulsants are drugs that are used to treat or prevent convulsions, i.e. the seizures seen in epilepsy. Phenytoin is the active ingredient of Epanutin (Nappi Code: 723525-005), Epanutin syrup (Nappi Code: 723533-016), Epanutin injection (Nappi Code: 723576-009), Epanutin Infatabs (Nappi Code: 723568- 006), Norstan-Phenytoin (Nappi Code: 754870-015) and Phenytoin Sodium 100 (Nappi Code: 754870-016/015).
- Pyrimethamine – In the US, Pyrimethamine (pyrimethamine systemic) is a member of the drug class miscellaneous antimalarials and is used to treat Malaria Prevention, Pneumocystis Pneumonia Prophylaxis, Toxoplasmosis and Toxoplasmosis – Prophylaxis. Brand names Fransidar and Daraprim
- Sulfasalazine – In South Africa, sulfasalazine is registered for the treatment of Intestinal inflammatory disorders. These include both acute and chronic ulcerative colitis, a serious disease that causes ulcers and irritation in the inner lining of the colon and rectum; and Crohn’s disease. It is also effective in treating rheumatoid arthritis, a crippling form of arthritis in which the body’s immune system attacks joints, causing hot, painful swelling and deformity. Sulfasalazine may reduce the absorption of folic acid into the body and an additional folic acid supplement may be needed. An active ingredient in Salazopyrin.
The good news is that high homocysteine levels can be managed through diet and vitamin supplementation. The most important nutrients that help lower homocysteine levels are folate, the vitamins B12, B6 and B2, zinc and trimethylglycine (TMG) or Betaine.

However, ordinary folate/ folic acid supplements might not cut it. One possible reason is that folic acid, the form of the vitamin used in most supplements and enriched foods, is not bioavailable enough to sufficiently increase plasma folate levels in people with certain health problems or genotypes, especially when you have an MTHFR issue.
Folic acid, as used in ordinary dietary supplements and vitamin-fortified foods, must first be converted to bioactive 5-methyltetrahydrofolate in order to be clinically effective. These steps require several enzymes, adequate liver and gastrointestinal function, and sufficient supplies of niacin (B3), pyridoxine (B6), riboflavin (B2), vitamin C, and zinc. Another advantage of 5-MTHF is that it is unlikely to mask a vitamin B12 deficiency, a shortcoming of folic acid. Folic acid, when administered as a single agent, may obscure the detection of vitamin B12 deficiency (specifically, folic acid may reverse the hematological manifestations of B12 deficiency, while not addressing the neurological manifestations).
Cooking and food processing destroy natural folates. Although red blood cells can retain folate for 40-50 days following discontinuation of supplementation, folic acid is poorly transported to the brain and is rapidly cleared from the central nervous system.
Researchers recently found that giving bioactive folate or 5-MTHF (5-methyltetrahydrofolate) to patients with coronary artery disease resulted in a higher plasma folate concentration compared with folic acid. This difference was irrespective of the patient’s genotype. Compared with bioactive 5-MTHF, folic acid supplements were relatively ineffective in increasing blood folate concentrations.